SECTION A
40 marks
Question 1
Students set up a photosynthesis experiment by placing aquatic plants into sealed tubes, submerging them in water. They measured the rate of photosynthesis by counting the bubbles that were produced by the plant. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. fewer bubbles would be produced by a plant that was placed in direct sunlight than a plant that was in a cool, dark room
B. the bubbles that the students measured were made of oxygen gas
C. the experiment needs to be repeated three times in order to be accurate
D. the water is only used to suspend the plants; it is not an input of photosynthesis
Question 2
In the body, cells that are infected with a virus present the viral antigen on their MHC-II proteins. These antigens can then be identified by lymphocytes as part of the specific immune response.
Which of the following lymphocytes would recognise a viral antigen that is displayed by body cells and what would be the next step in the immune response pathway?
A. a naïve B cell; a helper T cell will release cytokines to activate the naïve B cell
B. a naïve T cell; a helper T cell will release cytokines to activate cytotoxic T cells
C. a naïve B cell; the naïve B cell will undergo clonal selection, producing memory B cells and plasma cells
D. a naïve T cell; the naïve T cell will undergo clonal selection, producing memory T cells and cytotoxic T cells
Question 3
A non-competitive enzyme inhibitor will
A. bind to the active site.
B. attach to the substrate.
C. change the shape of the active site.
D. not work below 37°C.
Question 4
The key distinguishing feature between hominins and primates is
A. a large cranium relative to body weight.
B. opposable thumbs.
C. binocular eyes.
D. bipedalism.
Use the following information to answer Questions 5 and 6.
Below is a diagram of a nucleic acid involved in gene expression.
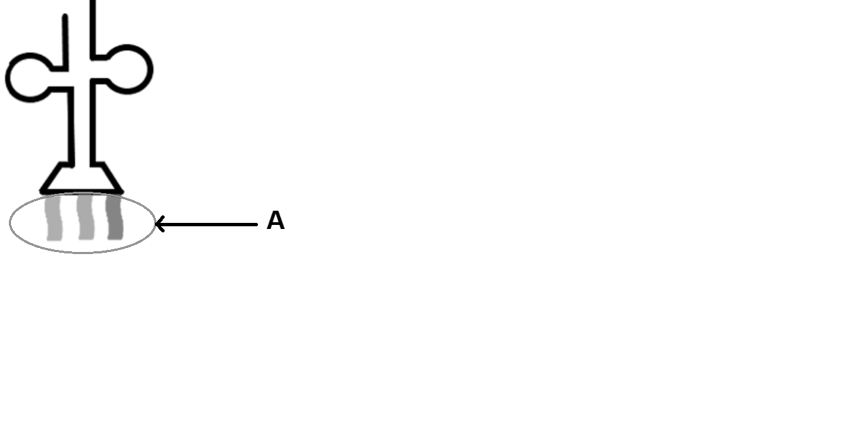
Adapted from Christinelmiller, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Question 5
Which option describes the role of this nucleic acid?
A. it encodes genetic information and carries it out of the nucleus
B. it moves genetic information into the nucleus
C. it brings amino acids to ribosomes
D. it is a component in ribosome structure
Question 6
In the diagram, what is indicated by ‘A?’
A. codon
B. anticodon
C. mRNA
D. deoxyribose nucleotide
Question 7
Homo sapiens’ larger brain size
A. is caused by the cerebrum becoming more folded.
B. has led to lesser social interaction and caregiving.
C. has reduced the energy needs of the human body.
D. is caused by an increase in the size of the sagittal crest.
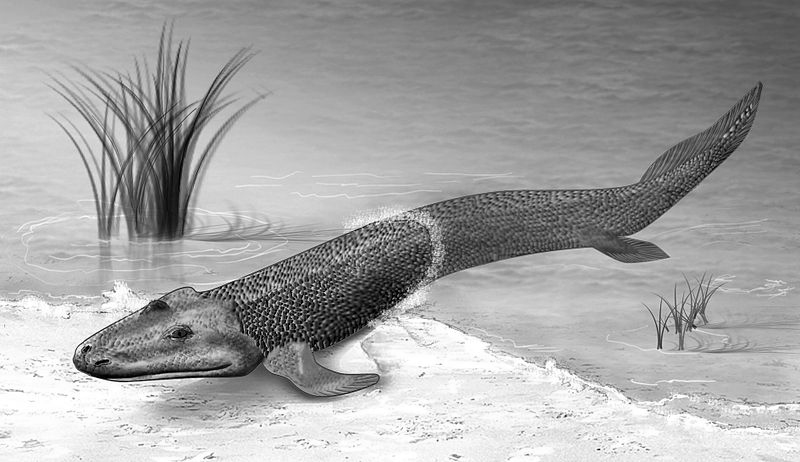

https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tiktaalik_roseae_life_restor.jpg
A fossil, known as the Tiktaalik fossil, was discovered in 2004. It had gills and fins, but it also had weight-bearing limbs. It is thought to be an evolutionary link between water- and land-dwelling species.
Question 8
Which of the following evolutionary timelines is in the correct chronological order?
A. prokaryotes, eukaryotes, multicellular organisms, water-dwelling animals, the Tiktaalik species, land-dwelling animals, mammals, flowering plants
B. prokaryotes, multicellular organisms, eukaryotes, water-dwelling animals, the Tiktaalik species, land-dwelling animals, mammals, flowering plants
C. prokaryotes, multicellular organisms, eukaryotes, mammals, water-dwelling animals, the Tiktaalik species, land-dwelling animals, flowering plants
D. prokaryotes, eukaryotes, multicellular organisms, water-dwelling animals, the Tiktaalik species, land-dwelling animals, flowering plants, mammals
Question 9
Which fossils provide an evolutionary link between previously identified species and known species?
A. trace fossils
B. index fossils
C. linking fossils
D. transitional fossils
Question 10
Which of the following options is not a requirement for fossilisation?
A. rapid coverage by sediment
B. cool climate
C. low light
D. high oxygen availability
Question 11
Which of the following statements about the inflammatory response is correct?
A. the steps in the inflammatory response are inflammation, vasodilation and migration
B. in the migration step, complement proteins and phagocytes work to destroy pathogens
C. vasodilation causes blood vessels to shrink and blood to build up, leading to swelling and redness at the affected site
D. mast cells signal natural killer (NK) cells
Question 12
When a fixed number of enzymes have an unending supply of substrate, their activity will
A. decrease because too much substrate availability will overwhelm the system.
B. continue to rise as long as there is an unending supply of substrate.
C. remain unchanged as only environmental factors, like temperature, can change the rate of enzyme activity.
D. rise until it reaches a plateau when no further enzymes are available.
Question 13
Which of the following is not a method of disease transmission?
A. airborne transmission
B. antibody transmission
C. vector transmission
D. faecal-oral transmission
Use the following information to answer Questions 14 and 15.
Insulin, as indicated in the diagram below, is a protein that is composed of two polypeptide chains (chains A and B) linked by disulphide bonds.
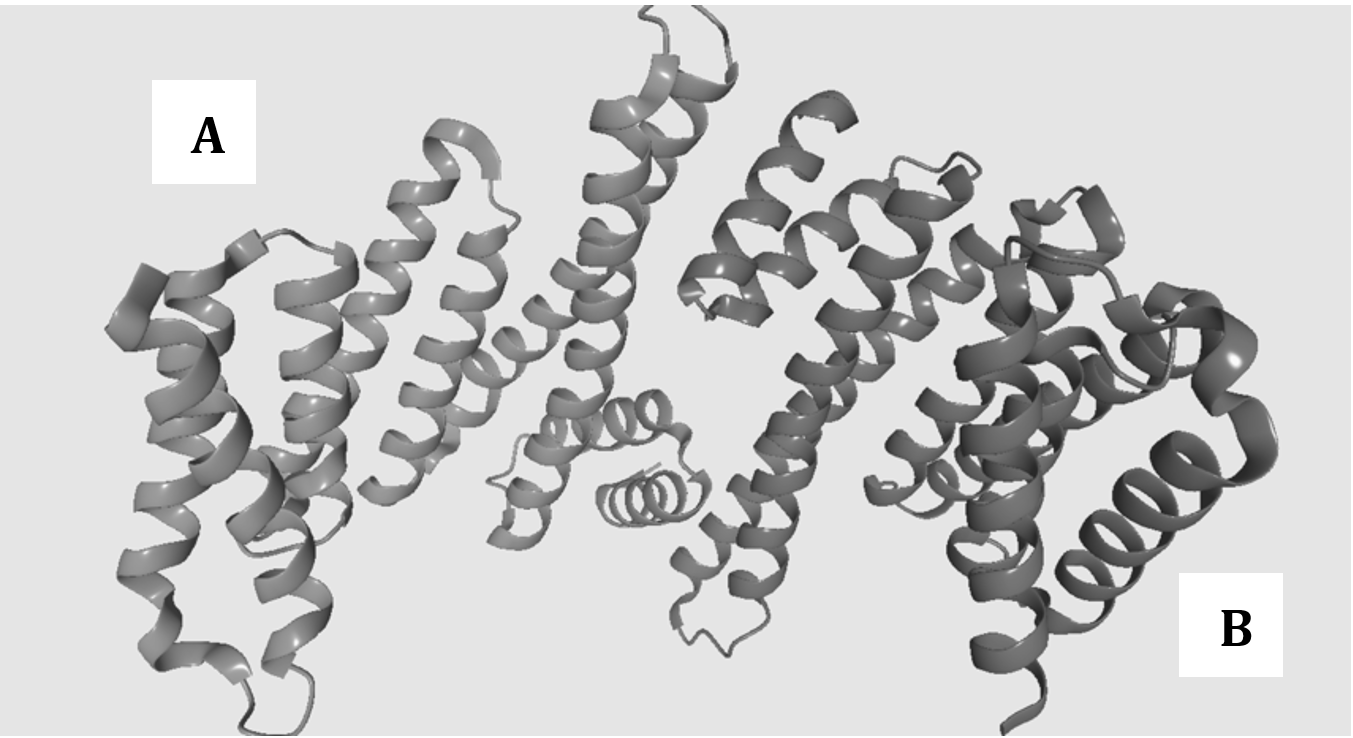
Adapted From: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/0c/2bq0_14-3-3.png
Question 14
What is the hierarchical level of the protein structure seen in chain A?
A. primary
B. secondary
C. tertiary
D. quaternary
Question 15
What type of protein is insulin?
A. a biochemical enzyme
B. a peptide hormone
C. a regulatory protein
D. a structural protein
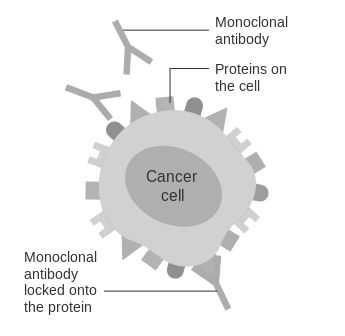
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Diagram_showing_a_monoclonal_antibody_attached_to_a_cancer_cell_CRUK_070.svg (Cancer Research UK)
Monoclonal antibodies, as seen in the diagram, can be used to treat cancer as well as other autoimmune diseases though a variety of approaches.
Question 16
The proteins on the cancerous cell to which monoclonal antibodies attach are known as
A. MHC-I proteins.
B. MHC-II proteins.
C. pathogens.
D. non-self antigens.
Question 17
Which of the following options is not an approach that monoclonal antibodies use to combat cancer?
A. binding to cancerous cells and marking them as foreign so that they are targeted by natural killer (NK) cells
B. binding to cancerous cells and interacting with complement proteins to form membrane attack complexes
C. binding to cancerous cells and interacting with helper T cells to induce the external apoptosis pathway
D. carrying radioactive isotopes or drugs to cancerous cells by conjugated monoclonal antibodies
Question 18
A patient receiving treatment with monoclonal antibodies receives what type of immunity?
A. natural passive immunity
B. artificial passive immunity
C. natural active immunity
D. artificial active immunity
Use the following information to answer Questions 19 – 21.
Barnacles are attached to rocks and cannot travel to avoid natural disasters or to mate with other barnacle populations.
A heatwave in a small coastal town led to the dark barnacles along the shoreline dying off. The lighter-grey barnacles were more likely to survive and now, the population is mostly comprised of light-grey barnacles.
Question 19
What occurred in this population?
A. natural selection
B. gene flow
C. bottleneck effect
D. viral drift
Question 20
What is unable to occur in the barnacle population due to its fixed position?
A. gene flow
B. natural selection
C. genetic drift
D. speciation
Question 21
How would the mass deaths of the dark barnacles and the barnacles’ fixed positions likely affect the genetic diversity of the barnacle population?
A. it would increase the frequency and number of unique alleles, leading to greater genetic diversity
B. it would reduce the frequency and number of unique alleles, leading to greater genetic diversity
C. it would increase the frequency and number of unique alleles, leading to lower genetic diversity
D. it would reduce the frequency and number of unique alleles, leading to lower genetic diversity
Question 22
What is the function of having an antibiotic resistance gene in a plasmid for bacterial transformations?
A. to activate the GFP gene in plasmids
B. to select for bacteria that have taken up the plasmid
C. to ensure that the gene of interest has been inserted into the plasmid
D. to kill off any recombinant plasmids
Question 23
Cat limbs and whale fins both developed from the same structures in shared ancestors, as indicated in the diagram below.
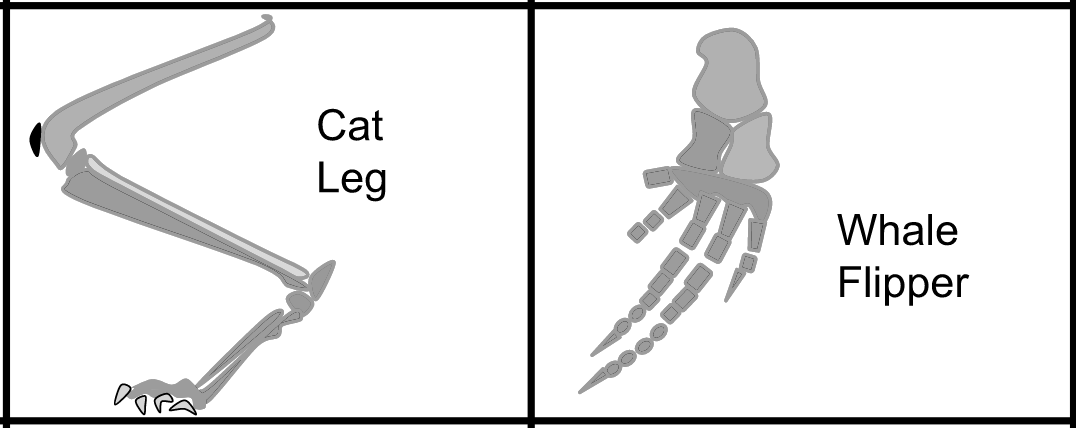
Adapted From: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/08/_Structures.svg
What is this an example of?
A. vestigial structures
B. homologous structures
C. analogous structures
D. trace structures
Question 24
Present day Europeans and Asians have around 1-3% neanderthal DNA. This suggests that
A. modern Homo sapiens are descended from neanderthals.
B. neanderthals and Homo sapiens experienced genetic drift between populations.
C. neanderthals and some humans lived at the same physical location at the same time.
D. neanderthals do not have mtDNA.
Question 25
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria pose a significant public health issue. Which of the following does not contribute to this issue?
A. natural selection acting on bacteria
B. overprescribing or inappropriately prescribing antibiotics
C. antigenic drift changing surface antigens
D. a patient stopping a course of antibiotics as soon as symptoms clear
Question 26
What is not a role of complement proteins?
A. attracting phagocytes to pathogens
B. releasing interferons to neighbouring cells
C. forming membrane attack complexes (MACs)
D. sticking to the outside of pathogens to aid recognition
Question 27
The light-independent reaction of photosynthesis
A. always occurs in mesophyll cells.
B. can only occur at low temperatures.
C. is also known as the Calvin cycle.
D. uses sunlight to split H2O.
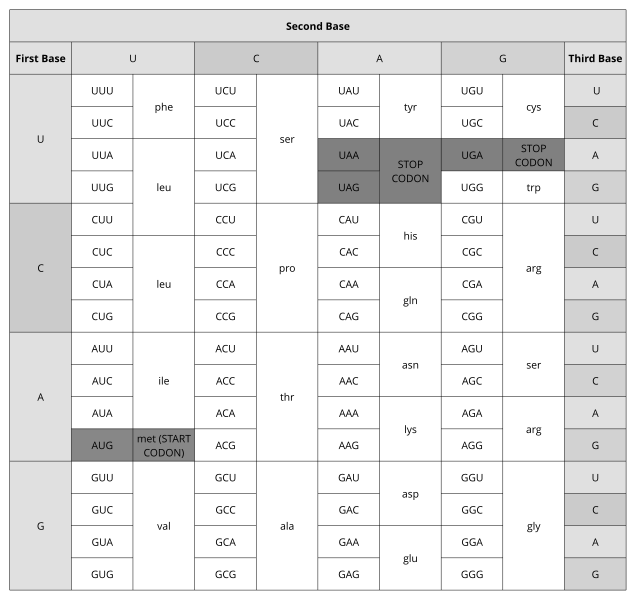
Use the following information to answer Questions 28 and 29.
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Amino_Acid_Codon_Table.svg
mRNA: CGAUGAAAACUACCUCGUAAGGAG
Question 28
What is the correct amino acid sequence that would be produced if the mRNA sequence above was translated?
A. arg
B. met – lys – thr – thr – ser
C. arg – cys – lys – leu – pro – lys – glu
D. met – lys – thr – thr – ser – tyr
Question 29
Which of the following correctly lists the movement of proteins after translation by ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
A. secretory vesicle, Golgi apparatus, transport vesicle, plasma membrane
B. Golgi apparatus, transport vesicle, plasma membrane, secretory vesicle
C. transport vesicle, Golgi apparatus, secretory vesicle, plasma membrane
D. plasma membrane, secretory vesicle, Golgi apparatus, excretory vesicle
Question 30
Which of the following is not a chemical barrier in animals?
A. acidic sweat
B. lysozyme enzymes in tears
C. stomach acid
D. cilia in the airways
Question 31
A study wanted to assess the effectiveness of a new antiviral drug on the severity of symptoms of adults infected with SARS Cov-19. Two groups of infected patients of equal size were created. One group received an antiviral drug and one group received just a sugar pill, alongside general monitoring of their health. The group that received the antiviral drug was the
A. control group.
B. experimental group.
C. independent group.
D. variable group.
Use the following information to answer Questions 32 – 34.
Scientists are attempting to create future-ready wheat by introducing drought-tolerance genes into the genome of common wheat (Triticum aestivum).
Scientists screened genes from common wheat crops that were grown in areas of low rainfall as well as Wild Emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccoides), which is known for its drought tolerance.
Question 32
Source: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/tswj/2013/548246/
Which of the following experiments conducted with common wheat will create a transgenic organism?

Question 33
The modified crops were then grown in threes in drought conditions at two temperature points. Wheat yields were measured at the end of the season.
Which of the following measurements are the most precise?

Question 34
Crossbreeding plants is an example of
A. selective breeding.
B. genetically modified organisms.
C. ethical maleficence.
D. natural selection.
Question 35
The genetic code is described as degenerate, meaning that
A. more than one codon codes for an amino acid.
B. it is the same in every organism.
C. it requires an mRNA copy of DNA to be made before translation can occur.
D. the genetic code is only made up of four bases.
Question 36
Which is the correct definition and example of the type of speciation provided?
A. Galapagos finches are an example of sympatric speciation; they developed into a new species without a geographic barrier
B. Galapagos finches are an example of allopatric speciation; they developed into a new species without a geographic barrier
C. Howea palms are an example of sympatric speciation; they developed into a new species without a geographic barrier
D. Howea palms are an example of allopatric speciation; they developed into a new species without a geographic barrier
Use the following information to answer Questions 37 and 38.
The below image shows a diagrammatic representation of the trp operon.
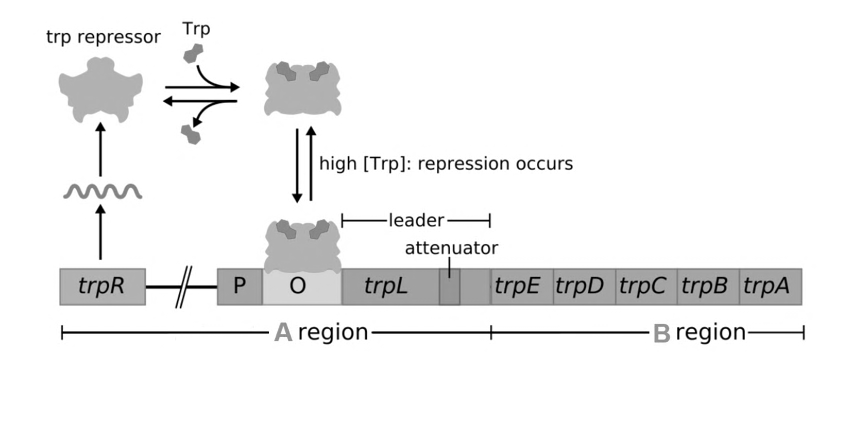
Adapted From: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Trpoperon.svg
Question 37
Regulatory genes
A. are shown in the B region of the diagram.
B. create proteins that assist in cell structure or proteins that perform roles around the body.
C. can code for proteins that stop gene expression.
D. only control the expression of a single structural gene.
Question 38
Which statement about the trp operon is correct?
A. structural genes will only be expressed when there is high cellular tryptophan levels
B. tryptophan molecules bind to RNA polymerase to change its shape and prevent transcription
C. when there are high cellular levels of tryptophan, an antiterminator hairpin will form in mRNA
D. a longer mRNA molecule will be produced when low levels of tryptophan are in the cell
Use the following information to answer Questions 39 and 40.
The table below and phylogenetic tree provided in Question 40 show the results of sequencing a 9- base pair region of the genomes of four species of fruit bat and comparing it to an ancestral sequence.
| Origin | Sequence |
| Ancestral sequence | GCGATCTGC |
| Species A | GCCATCTGC |
| Species B | GCAATGTCC |
| Species C | GCTATGTCC |
| Species D | TCGATCTAC |
Question 39
What type of mutations occurred between the ancestral sequence and the sequence in Species C?
A. frameshift mutation
B. point mutation
C. block mutation
D. somatic mutation
Question 40
Which phylogenetic tree correctly represents the data from the table?
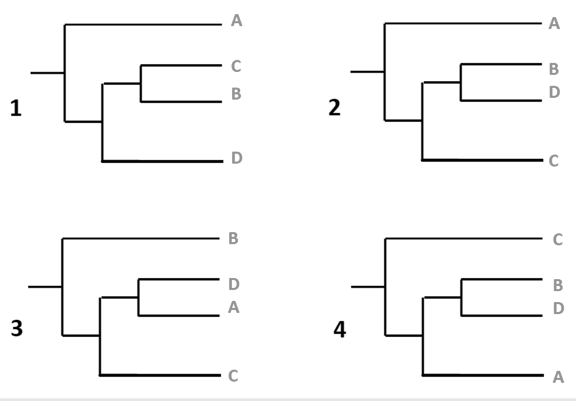
A. tree 1
B. tree 2
C. tree 3
D. tree 4
SECTION B
80 marks
Question 1 (12 marks)
Scientists in Melbourne have been experimenting using CRISPR in mice to inactivate a mutated version of the GG1 gene that they believe may be disease-causing in humans and mammals. In mice, the GG1 gene is 2380 base pairs (bp) long. The mutated variation known as GG1-B is 2930 bp long.
Scientists screened baby mice for the GG1-B variant using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to target and amplify the gene.
The results for four different mice (A, B, C, D) were run on gel electrophoresis alongside a standard ladder – these results are included in the image below.
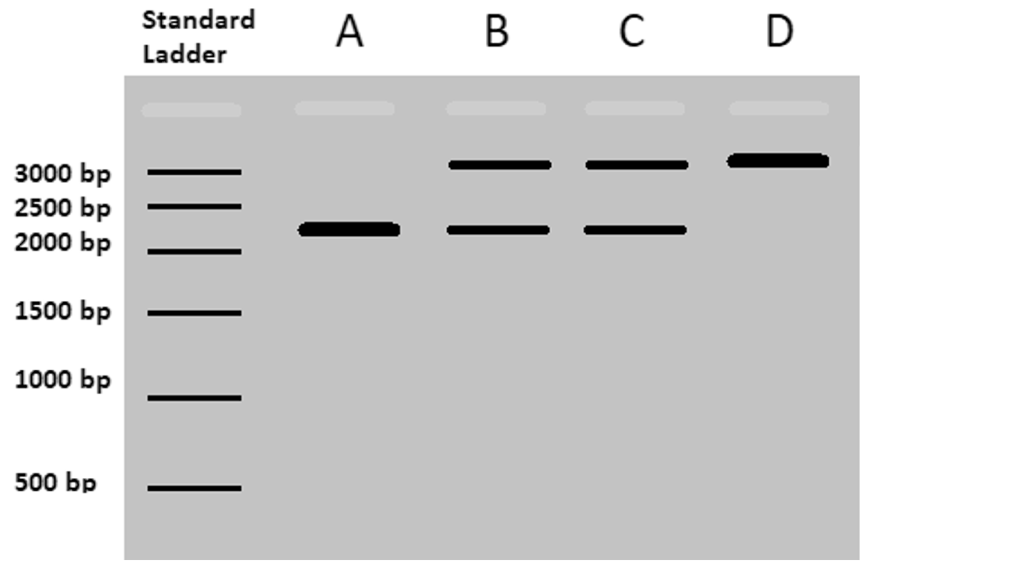
a. Which of the four mice is homozygous for the GG1-B variant? Justify your answer. 3 marks
b. Outline the steps of a single cycle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR). 3 marks
c. Name the component that acts as the endonuclease during CRISPR-Cas9 and explain why it does not work like a typical restriction enzyme.
2 marks
d. Scientists are exploring the potential of using CRISPR-Cas9 for gene editing in humans. Describe two potential ethical issues with using CRISPR-Cas9 to eliminate genetic diseases.
2 marks
e. Using CRISPR to correct the genetic basis of inherited genetic diseases is mainly suggested for embryos. Explain why this process would be most effective in embryos as compared to adults.
2 marks
Question 2 (5 marks)
a. State the total ATP yield produced by one molecule of glucose in aerobic cellular respiration.
1 mark
b. Name the regions ‘A’ and ‘B’ that are indicated in the below diagram and name the cellular respiration process that occurs at each part.

2 marks
c. Name the molecule that glucose is broken down into during glycolysis, and name the further derived molecule that is an input of the Krebs cycle.
2 marks
Question 3 (11 marks)
Vaccination for COVID-19 is one of the main forms of combatting the disease and controlling spread. COVID-19 vaccines either introduce or have the body create a fragment of the disease to which the immune system responds, building immunity for future infections.
a. How does the lymphatic system streamline the recognition of the viral antigen? 1 mark
b. Outline the steps that occur in the cell-mediated immune response that leads the body to produce cytotoxic T cells when it encounters a viral antigen.
4 marks
c. Describe why having a majority of people being vaccinated and gaining herd immunity is important in combatting and controlling disease.
1 mark
d. List three measures, other than vaccination and herd immunity, that may be used to control and/or screen disease transmission.
3 marks
e. Describe antigenic drift and outline how it can impact the effectiveness of a vaccine. 2 marks
Question 4 (8 marks)
The basis of the ‘Out of Africa’ model is that Homo sapiens evolved first in Africa and then spread around the world between 100,000 and 200,000 years ago, superseding all other hominin species.
Modern humans had reached Asia approximately 70,000 years ago before moving down through South-east Asia and into Australia approximately 50,000 years ago. Homo sapiens, however, were not the first hominins to inhabit this region; Homo erectus had already been in Asia for at least 1.5 million years.
The remains of an Indigenous man, dubbed ‘Mungo Man,’ was discovered in a lake from the World Heritage-listed Willandra Lakes region in far-western New South Wales. The remains have been dated to be over 40,000 years old.
Source: https://australian.museum/learn/science/human-evolution/the-spread-of-people-to-australia/
ai. Radiocarbon dating can be used for organic samples up to 60,000 years old.
What is the half-life of carbon-14?
1 mark
aii. Radiocarbon dating determines numerical age for fossils and other materials. Can this be considered absolute or relative dating?
1 mark
b. Researchers attempted to extract mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) from Mungo Man and sequence it; however, further research has discovered that the sample had been contaminated with modern human DNA, likely from people handling the bones.
What kind of scientific error is this? Justify your answer.
2 marks
c. Why is mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) especially useful for determining evolutionary relationships?
2 marks
d. Does the discovery and dating of the Lake Mungo remains directly impact or contradict the ‘Out of Africa’ hypothesis? Justify your answer.
2 marks
Question 5 (13 marks)
Biochemical processes such as photosynthesis require enzymes and coenzymes to facilitate and speed up reactions.
a. Write the unloaded form of ATP and describe its role in the light-dependent and light-independent stages of photosynthesis.
3 marks
b. Rubisco is an enzyme in photosynthesis that fixates carbon. If it binds to the wrong substrate, Rubisco undergoes a process called photorespiration.
Name the alternate substrate that Rubisco may bind to and outline the effect that this has on photosynthesis.
2 marks
c. The two key factors that determine whether Rubisco undergoes carbon fixation or photorespiration are temperature and substrate concentration. A team was studying the impact of these different environmental factors on Rubisco enzyme activity. The results from one of their experiments is shown below.

Referring to the graph, what change was made at nine minutes? Justify your answer, referencing the data.
3 marks
d. When designing their experiments on factors that affect enzyme activity, the team were careful to only test one factor at a time.
Given this approach, if the substrate concentration was being changed between groups in the experiment, explain what should happen to the temperature and why.
2 marks
e. Changing weather conditions, including rising temperatures and water unavailability, can increase photorespiration in plants. While 85-90% of plants undergo regular photosynthesis, some plants have adaptations to decrease photorespiration and maximise photosynthesis.
Sources: Khan Academy (https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/photosynthesis-in-plants/photorespiration—c3-c4-cam-plants/a/c3-c4-and-cam-plants-agriculture); Science Direct (https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/c3-photosynthesis (taken from A.S. Raghavendra, in Encyclopedia of Applied Plant Sciences, 2003))
Describe the adaptations of C4 and CAM plants to maximise photosynthesis.
3 marks
Question 6 (10 marks)
Galapagos finches developed into different species after they dispersed across different islands, creating geographic isolation between the Finch populations.
a. What type of speciation is this? Describe the process. 4 marks
b. Small groups of finches from an island group would be able to cross large distances with the right wind.
Identify the term for when a population is seeded by a small group of individuals with different allele frequencies to the main population.
1 mark
c. Outline the steps of natural selection for the Galapagos finches. 3 marks
d. Over a long period of time, with little change in selection pressures, how is natural selection likely to affect genetic diversity? Why is this the case?
2 marks
Question 7 (4 marks)
The first European settlers in Australia brought with them infectious diseases that severely impacted the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander populations, resulting in mass infections and death.
“Smallpox spread across the country with the advance of European settlement, bringing with it shocking death rates. The disease affected entire generations of the First Nations populations and survivors were in many cases left without family or community leaders.” (National Museum of Australia)
Source: https://www.nma.gov.au/defining-moments/resources/smallpox-epidemic
a. Give three reasons why smallpox and other European diseases would have had such a severe impact on the First Nations populations.
3 marks
b. One of the main symptoms of smallpox is a fever. What is the purpose of a fever in the body?
1 mark
Question 8 (8 marks)
Biofuels that are made from biomass are considered to be a potentially greener alternative to fossil fuels.
Source: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/65086
a. Give two reasons why biofuels are considered more environmentally friendly than fossil fuels.
2 marks
b. What are two of the required environmental factors to induce anaerobic respiration?
2 marks
c. List the biofuel that can be made by anaerobic fermentation and one application of this fuel.
2 marks
d. List the outputs of anaerobic respiration for plants/yeast as opposed to animals. 2 marks
Question 9 (5 marks)
a. Outline the steps in the process of transcription. 3 marks
b. Describe how a single gene can produce multiple different mRNA strands. 2 marks
Question 10 (4 marks)
Humans have two sets of chromosomes (i.e., humans are diploid). It is common for plants to have more than two sets of chromosomes; this can be advantageous, especially to crop plants, due to increased heterozygosity and as this can protect against the effects of deleterious mutations. It also, however, often results in reduced fertility due to meiotic errors, allowing for the production of seedless varieties.
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wellington-Clarindo/publication/288831058_The and_its_key_role_in_plant_breeding/links/568bf43308ae8f6ec752430a/The-and-its-key-role-in-plant-breeding.pdf
a. Common in plants, what is the term for having multiple sets of chromosomes? 1 mark
b. What term is used to describe having one or more chromosomes missing from a set of chromosomes, or having one or more additional chromosomes?
1 mark
c. Plants with high yields or desirable traits, such as seedless fruit, have been developed using genetic modification (GMO), but some consumers and farmers have rejected GMO products and crops.
Outline one concern and one benefit regarding GMO crops.
2 marks
END OF QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOK
Extra space for responses
Clearly number all responses in this space.
VCE BIOLOGY
Written Examination
ANSWER SHEET – 2022