nucleic acid
A nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. It is acidic and resides in the nucleus of cells, so that’s its name.
Nucleic acids contain the genetic information in all cells.
| DNA | RNA | proteins | carbohydrates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| monomers | nucleotides - adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine | nucleotides - adenine, guanine, cytosine, urasil | amino acids | monosaccharides |
| encodes genetic information | yes | yes | no | no |
| structure | double helix | single helix | ||
| catalyzes biological reactions | no | yes | yes | no |
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polymer of nucleotides.
is a nucleotide that contains deoxyribose
DNA has high stability compared to RNA due to having thymine instead of uracil.
DNA provides instructions for how and when to make the many proteins needed to build and maintain functioning cells and tissues
In eukaryotic cells, DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell, and the DNA is linear and free floating.
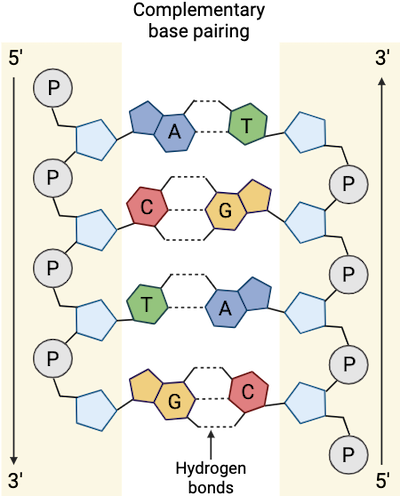
Figure: DNA strands are antiparallel, meaning that one strand goes from the 3’ (three prime) end to 5’ (five prime).
RNA
RNA is single stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds. A ribonucleotide in the RNA chain contains ribose (the pentose sugar), one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, and C), and a phosphate group.
references
https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/biomolecules/dna/a/dna-structure-and-function